AWS Lake Formation privilege import #
Starburst Galaxy supports reading privileges from your AWS Lake Formation account. These permissions integrate with Starburst Galaxy’s access control system to ensure fine-grained security across all your catalogs and other entities.
Prerequisites and limitations #
- The integration only supports privileges managed by AWS Lake Formation, not
AWS IAM policies. Furthermore, the special
IAM_ALLOWED_PRINCIPALSprincipal is not supported. - We recommend that the credentials supplied for the AWS Glue metastore have
AWS data lake
administrator
permissions. Specifically,
GetDataLakeSettings,ListPermissions, andListLFTagspermissions are required. - It is recommended that the credentials be an explicit AWS data lake administrator. Only permissions that are viewable by the AWS data lake administrator principal are imported to Galaxy. The IAM role or user supplied in the credentials cannot indirectly receive data lake administrator privileges via group membership.
- The Starburst Galaxy role used to create the catalog must have the Manage security and Create catalog privileges.
- Permissions granted to AWS service roles are not read.
- Galaxy accounts are limited to 100 IAM principal imports.
- Lake Formation tag-based access control privileges and Lake Formation data filters are not imported.
Configure Lake Formation integration #
To use AWS Lake Formation privileges in Galaxy, create an S3 catalog using the AWS Glue metastore, and click Import AWS Lake Formation permissions.
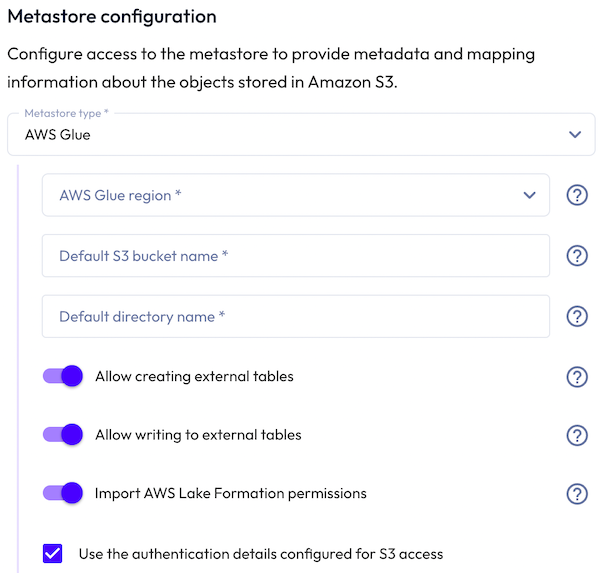
After you create an AWS Glue catalog, Galaxy reads AWS Lake Formation privileges asynchronously. Galaxy imports privileges once. Privileges are not synced automatically. However, you can trigger a manual re-read from the catalog’s vertical ellipsis menu in the Catalogs pane.
After a catalog has been created, it is not possible to modify the setting to read AWS Lake Formation privileges.
Lake Formation privileges in Galaxy #
Starburst Galaxy uses the information from the AWS Lake Formation permissions model to grant the relevant Galaxy privileges on the catalog when read. These roles and privileges can be viewed at any time from the Roles and privileges pane for roles with the Manage security privilege.
All supported IAM roles, users, and groups are imported as Galaxy roles. Imported roles are not automatically granted to any other role or user. Imported roles must be granted to other groups, users, or roles in Galaxy after the AWS Lake Formation privilege import has completed. These grants persist across imports.
There are slight semantic differences between AWS Lake Formation privileges and Starburst Galaxy’s privilege model:
- In AWS Lake Formation, a database equates to a schema in Starburst Galaxy.
- In Starburst Galaxy,
ALTERandDROPpermissions are limited to the entity owner and are not imported. Galaxy limits ownership of a catalog, schema, or table to a single role. Refer to the ownership topic to update ownership for any schema or table in the catalog. - Principals with AWS Lake Formation’s
INSERTpermission haveINSERTandUPDATEGalaxy privileges. DESCRIBEpermissions are not imported. In Galaxy, a role has the equivalent ofDESCRIBEif they have one privilege on the entity; for example, usingSELECTon a table impliesDESCRIBE.
Is the information on this page helpful?
Yes
No